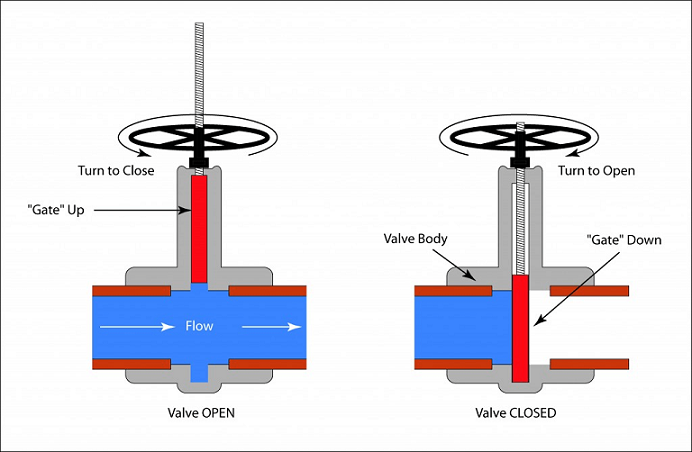
A valve is a mechanical device used in various industrial applications to control the flow of liquid and pressure within a system. Many types of valves are specifically designed to perform one or more of the following functions:
- starting and stopping fluid flow
- controlling the direction of fluid flow
- relieving component or piping overpressure
- throttling the amount of fluid flowing through the system
- regulating downstream system or process pressure
Most valves designed to regulate the flow consist of mechanical devices calledactuators. These devices are designed to operate the valve’s closure element to open and close its flow as and when required. They can be used from a remote location, thus eliminating the need for operators to go to every valve to reposit it manually. An actuator is connected to a power source to operate the valve; this power source can be hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric. While in the case of hydraulic, a pressurized fluid is used to control the valve movement. In pneumatic, pressurized air is used to operate a valve; electric systems use electric motors and solenoid-actuated valves.
Types of actuators
There are two types of valve actuators, namely – linear and rotary.
Linear valve actuators
Linear valves need an actuator that produces linear motion to operate the valve. These are entirely different from a rotary actuator. This is because linear valves such as pinch, gate, globe, and diaphragm valves perform various functions compared to rotary valves. Therefore, these are sliding stem designs that push the closure element to open or close the valve.
Rotary valve actuators
As the name suggests, a rotary valve actuator produces the rotational motion required to operate rotary valves (such as butterfly, plug, and ball valves). It rotates the valves to a quarter-turn or more from open to close. They come in many different designs, and each one offers its advantages.
Functions of actuators
Regardless of the method of actuation, all styles of actuator perform several basic functions that include:
- Maintain the position of the closure element: The valve actuator must be able to keep the closure element in the desired position. Depending on its type, it may use spring, fluid, or mechanical stiffness.
- Operate the closure element: A valve actuator should be able to provide the necessary force to move and position the closure element even under demanding process conditions.
- Operating at an appropriate speed: The cycle speed of an actuator is manageable via control elements, but if you require cycle speed to be less than half of the basic actuator cycle time, you need to select special pneumatic actuators that provide a high cycle speed.
- Providing adequate rotational capabilities: It must provide proper rotation capabilities (generally 90 degrees or 180 degrees) depending on its type and application.
- Seating the valve with sufficient torque: Some applications may require unique components for actuator sizing to sustain enough torque and maintain closed positions.
- Having a failure mode: Failure mode occurs when the system fails, or power fails. The valve actuator should have a proper failure mode to ensure the system does not experience excessive damage.
Things you need to consider when choosing valve actuators
The essential considerations to weigh when choosing valve actuators are:
- Usage factors (compatibility, power source available, temperature range, and associated risk in application area)
- Sizing and force (this would be determined based on the minimum and maximum supply pressure, type of actuator, failure mode, and valve torque)
- Speed of the operation (whether you are getting it for faster operations or slower operations)
- Frequency of operation (it will determine the durability and robustness of the system)
- Safety and cost